Nearly everyone everywhere has seen a barcode today. Barcode’s have revolutionized the way we package and transport merchandise. A barcode, by
Investopedia.com’s definition, is a graphical representation of a product’s identifying information formed by two-dimensional pattern of black and white stripes. They are used to automate the transfer of product information from the product to an electronic system, or cash register.
Barcode Scanners capture and read this information and come in many different forms, depending on the needs of the user.
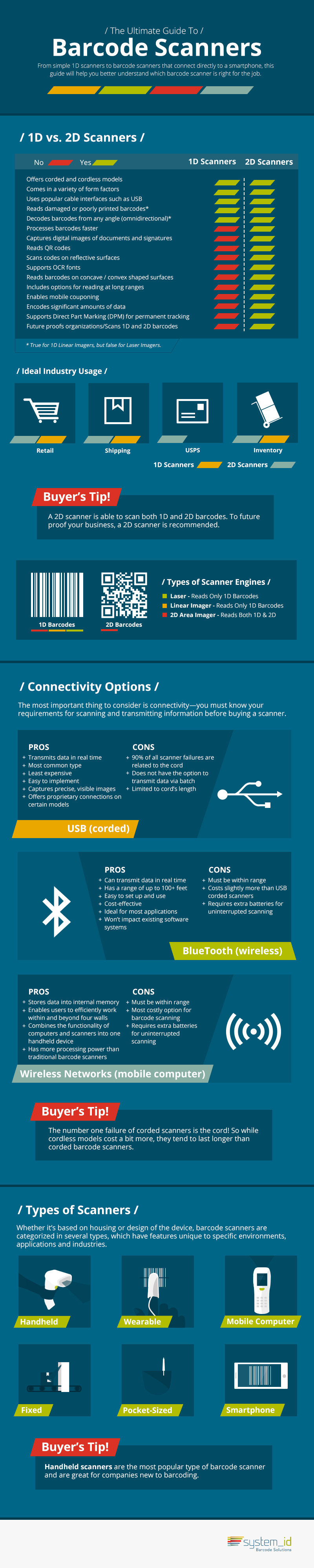
Barcode scanners automate the identification and tracking of products, people, inventory, and assets for ultimate efficiency and transparent compliance across the supply chain. Barcode scanners, or barcode readers, use laser, linear imager, or 2D area imager scan engines to capture images and transmit them to a host computer. With many different varieties available to your industry today, it’s important to understand their differences in order to make the most out of your investment in barcode scanners.

Laser Barcode Scanners
The most popular type of barcode scanner, and most widely used, is the
laser barcode scanner. Affordably priced and able to read 1D linear barcodes from a distance of up to 3.5 feet away, laser barcode scanners come in a variety of form factors from
handheld devices to wearable and
pocket-sized. Today there are different models and configurations for every industry and environment. They are most commonly used by retailers and grocers.

Linear Imager Barcode Scanners
A more durable option than laser barcode scanners are the
linear imager barcode scanners. These scanners are better for reading damaged or poorly printed barcodes, or barcodes under plastic film or covering. Linear barcode scanners are ideal for retail, shipping, receiving, and inventory applications.

2D Barcode Scanners
The holy grail of barcode scanners includes
2D barcode scanners, with the ability to read both 1D and 2D barcodes regardless of damages, orientation, or covering. 2D Scan engines take a picture of the barcode, which makes these scanners ideal for environments requiring reliability and flexibility. Since 2D barcode scanners are omnidirectional, the capture speed and accuracy is heightened than with other scanners. The maximum productivity of 2D barcode scanners makes them appropriate for most any environment, including retail, manufacturing, and postal/courier services.